
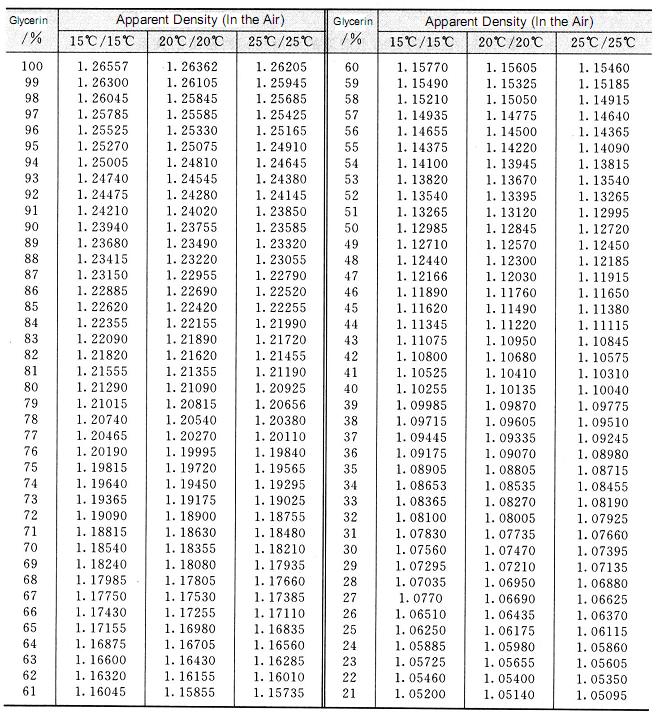
When choosing between the two viscosities, it is worth noting that dynamic viscosity tells us about the force required to move the fluid at a certain speed. 9 (1951), p2117.The larger the force or stress needed to move the plate, the more viscous the fluid is. Viscosity of Aqueous Glycerine Solutions in Centipoises/mPa s Temperatur e (☌)Glycerine percent weight 0 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 90 100 0 (1) 1.792 1.308 1. Oberstar, Industrial & Engineering Chemistry, V43, No. The variations of viscosity, surface tension and density at different glycerol concentrations are shown in Figure 1, where 0 Vol. The comparison shows that with this experimental approach using an optical tweezers technique, the viscosity of water-glycerol mixture is determined to an accuracy of 0.0082 percent. The experimental results are compared with the work of Segur and Oberstar as well as with a simple theoretical approach that models the data behavior versus glycerol concentration. Using this approach, the viscosity of a water-glycerol mixture has been measured for glycerol volume concentration of 10%, 20%, 30%, and 40%. 1 Material Safety Data Sheet 2 Structure and properties 3 Thermodynamic properties. The high exibility and viscosity of glycerolmake it an important system in studies of the glass transition.17Also, glycerol has been used to preserve proteins because of itscryoprotective properties18and to stabilize enzyme activities.2,3The ability of glycerol to form hydrogen bonds with watermakes glycerolwater mixtures fascinating solutions. By following an iterative experimental approach, the viscosity of the water-glycerol mixture can be obtained by comparing the corner frequencies obtained experimentally in a medium of known viscosity. This page provides supplementary chemical data on glycerol. Drag Coefficient The drag coefficient quantifies the drag or resistance of an object in a fluid environment. For a small change in volume concentration of glycerol in a water-glycerol medium, the change in trap stiffness can be ignored if incident laser power and bead radius remain unchanged. Viscosity at 20C/68F and 50C/122F for more than 120 crudes is shown as function of specific gravity15C/60F. By using a Lorentzian fit to the Power Spectrum of the position signal, the corner frequency is obtained. Since various properties of alcohol water mixtures such as density, boiling or melting point, viscosity, and dielectric constant are determined by their. In this approach, the position of a trapped bead of radius r in a glycerol-water mixture is measured using a position sensing diode with 40 kHz acquisition rate. In order to understand the viscoelastic nature of a medium, we have developed a new simple approach to quantitatively measure the viscosity of water-glycerol mixture medium using an optical tweezers technique. Besides, the volume thermal expansion coefficients are also calculated. In many instances, the liquid will be a mixture of one or more components. These, together with their value for water, were used in constructing a table of viscosities corresponding to specific gravities from 1.000 to 1.260 a t. The effe ct of temperature on different volumetric properties studied is also analyzed. A cellular medium is highly viscoelastic in nature. Viscosity and surface tension are key physical parameters in a variety of flow phenomena, including bubble and droplet break-up and capillary wetting.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
